Common Testing Terms and Definitions for Foam Materials

This article provides an overview of common testing terms and methods for foam materials, covering key properties like hardness, resilience, tensile strength, elongation, and tear strength, ensuring accurate assessment across various foam applications and industries.
Fire Prevention in PU Flexible Foam Production and Usage

This article outlines essential fire prevention measures in PU flexible foam production and usage, including incorporating flame retardants, managing curing processes, cutting, crushing, adhesive processing, and ensuring electrical and hot work safety, to mitigate fire risks effectively.
Applications of Solvent Oils in Polyurethane Release Agents

This article explores the role and evolution of solvent oils in polyurethane release agents, highlighting their importance in manufacturing, changes over time due to environmental and safety regulations, and advancements leading to more efficient and eco-friendly alternatives.
Polyurethane Foam Foaming Common Terms

This article explains key terms and processes in polyurethane foam production, including Cold Cure, Pump Capacity, Pump Linearity, New Blending Technology (NBT), Timed Pressure Release (TPR), Initial Spray, and the Foaming Index.
How to Test the Standards for Polyurethane Foam Foaming?

This article outlines the standards and methods for testing polyurethane foam, covering key properties such as density, hardness, tensile strength, tear strength, resilience, compression deformation, fire resistance, and VOC emissions.
What is the difference between high-density and medium-density PU soft foam

In the foam industry, PU flexible foams are grouped by density (KG/M3): high-density for sound absorption, sofa cushions, and soft packaging; medium-density for protection. High-density foam (≥45) with abundant pores is versatile, while medium-density foam (45-18) is widely used for protective purposes.
What is the difference between high-density foam and high-resilience foam?
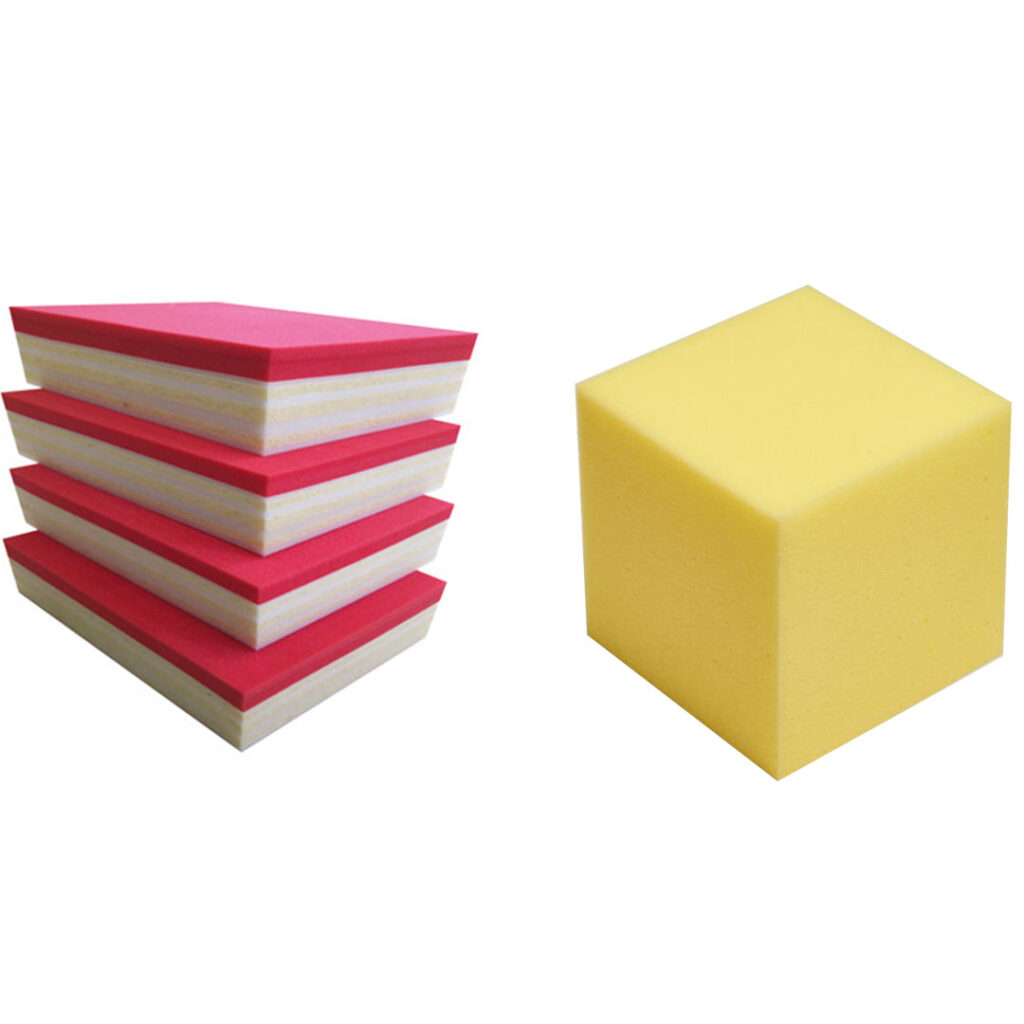
The difference between high-density foam and high-resilience foam lies in density and structure. High-density foam, suitable for sound-absorbing cotton and soft packaging, has high density and greater mass. On the other hand, high-resilience foam, made with polyether polyols, boasts excellent resilience and breathability, primarily used in car seats and furniture. The two types differ significantly in principles, applications, and characteristics.
What are the factors that affect the resilience of PU foam?

Factors affecting the resilience of polyurethane foam include: 1. Cell opening rate; 2. Cell shape; 3. Cell pore size and distribution; 4. Polyether polyol; 5. Isocyanate; 6. Other factors.
Production Process and Principles of Polyurethane Foam

This article introduces the production process and principles of polyurethane foam, including main raw materials, synthesis principles, and the production process. It covers the characteristics of flexibility, elasticity, and water absorption in polyurethane foam, widely used in furniture and decorative industries.
What are the two main stages of polyurethane foam formation?

The molding of polyurethane foam involves two stages: the foaming process and the curing process. The process from the mixing of raw materials to the cessation of foam volume expansion is known as the foaming process
